Video analysis
Video analytics refers to all solutions whereby the video surveillance system automatically performs an analysis of the captured video footage. The applications that provide this analysis service are also referred to as video data analysis (VCA) or video analytics (VA).
Today, video data is recorded in large quantities, but only a fraction of the material is ever viewed or reviewed. Important events can be missed without the use of video analytics. Incidents and unwanted activities are not detected or prevented in time.

Reduction of network load as well as storage requirements
The use of video analysis reduces storage requirements and the network load enormously, since recording only occurs when activities are detected. Such analysis algorithms are integrated in modern cameras. The video material is processed and forwarded automatically. Thus, video analysis actively contributes to improving the efficiency of a video system.
The larger the video surveillance system, the more difficult it is to keep track of it. Especially the nowadays common multi-monitor operation of modern video systems makes it difficult for the staff to keep an eye on what is happening. By using intelligent video analysis, a few employees can monitor very large facilities, as undesirable occurrences are detected automatically.
Intelligent video systems support the work of personnel and inform them, for example, about people in areas with access restrictions, about wrong-way drivers or about any attempts to tamper with surveillance cameras.

Video analytics to determine memory requirements
Here you will find a listing of surveillance cameras as well as the required capacities for a recording with different transmission rates.
Faster video retrieval
Searching stored video footage for incidents is very time-consuming, as personnel have to view the entire recording. For this reason, it is usually kept and deleted after a certain time.
By using video analytics, e.g. motion detection, only relevant video footage is stored by recoding only when triggered by motion or other triggers. If old recordings need to be searched, only material that can potentially contain the incident in question is retrieved. In addition, intelligent video systems that, for example, tag the video stream as it is recorded, can automatically search through several days’ worth of video footage and find the right location within seconds.
Mit dem Laden des Videos akzeptieren Sie die Datenschutzerklärung von YouTube.
Mehr erfahren
Video analysis in detail
The application areas of powerful video analytics are diverse and go far beyond normal video surveillance. New analysis functions are constantly being added and, especially in the field of artificial intelligence, many ideas are finding usage in everyday life in the video surveillance industry. However, the majority of all video analytics users rely on well-proven technologies:
Object detection
The system detects objects in a scene. The classification follows.
Object classification
The system distinguishes between, people, vehicles, etc.
Object attribute detection
Attributes are assigned to the recognized object. For cars e.g. color, for people e.g. glasses…
Face recognition
The AI can tell if a person has access to an area or not based on their face.
Gender recognition
Recognition of the gender of a person is possible without any problems.
Age Recognition
The classification to an age group is done automatically.
License plate recognition
License plate recognition can be performed alongside normal video surveillance tasks thanks to AI.
People counting
Thanks to reliable object detection, people counting operates even more reliably. The walking direction is also recorded and can be evaluated.
Mask recognition
In sensitive areas, masks are still required. KI reliably detects if the mask is properly fitted.
Improved search
Video management systems also exploit the possibilities of AI. For example, search for cars, people, and more.
Relevant Data Storage
Through intelligent object classification and attribute recognition, only relevant data such as faces, license plates or similar can be stored.
Social Distancing Detection
If the minimum distances are not maintained, the video system reliably reports where personnel must intervene.
Understanding customer behavior with video analysis
Video analytics allow video surveillance systems to be used for areas beyond security.
In retail stores, for example, they can be used to analyze customer behavior, e.g., how many customers stop in front of a particular shelf or how most customers move through the store (heat maps).
At airports, intelligent video systems can measure how long travelers wait at the check-in counter. This data can be directly utilized by staff and shorten travelers’ waiting time.
Intelligent video systems offer multiple additional uses for the video surveillance infrastructure, ensuring a high return on investment (ROI).

Video analysis in retail
For you, video surveillance and video analytics probably mean security and loss prevention. However, your VTIS video system can do more than you think. You can also use intelligent video analysis to increase your sales and reduce costs.
Win customers
Attracting customers is essential for any retail business. Making customer acquisition more efficient can be a real challenge. Studying buyer conversion rates is a first approach. It is achieved by capturing and measuring buyer traffic to create sales opportunities. This, in turn, reveals ideal opportunities to turn prospects into customers.
By using a traffic count, retailers can increase conversion rates and revenue by making adjustments to business processes. For example, staffing can be optimized by identifying specific days or times of day.
Motivate to buy
A solid understanding of how displays can be optimized to motivate customers to interact is essential. Retailers should always try to do more to entice shoppers to stop in front of displays to buy products.
The following questions should be asked: How many people come and at what times do they come? What displays motivate people to buy? Is there staff on the sales floor and how many customers bought something that day? Using a shopper analytics solution can help to answer these questions and analyze the results.
Increase conversion rates
The amount a customer spends is directly related to their personal shopping experience. Currently, in-store conversion rates are below 30 percent and falling. To reverse this disturbing trend, retailers must constantly re-evaluate their store layout, product assortment, and execution of special promotions or special offers to improve conversion results. With our video analytics solutions, retailers gain an understanding of these relationships and can more effectively attract potential shoppers to their stores.
Understanding customer needs With the help of video analysis
Use your in-store cameras to capture and process numerical data. This allows you to track, understand and predict your customers’ behavior and needs using statistical techniques. Unlock the full potential of your business.
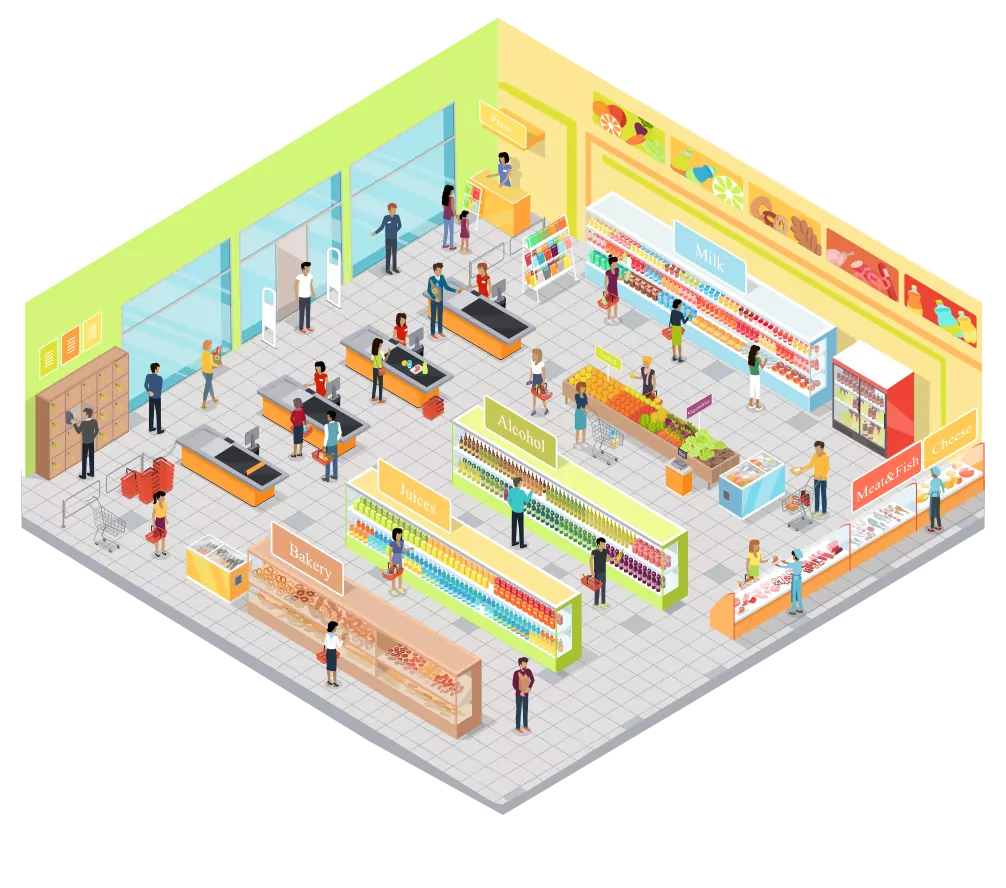

Sales area
Track customers moving through your store and identify high-traffic areas.
Optimize your store layout based on this information and send targeted audio messages and promotional announcements to the right place at the right time.
Analyze your retail space by measuring visitor density and frequency in defined areas.
Queues & cash registers
Determine the number of people waiting in line and automatically assign more staff as needed
Inputs & Outputs
Daily people counting allows you to identify peak times in your store, allowing you to deploy staff more efficiently and optimize service levels.
Display ranges
Detect customers when they are in your most profitable areas and alert sales staff via audio message.
Optimize focus areas
with video analysis

Mit dem Laden des Videos akzeptieren Sie die Datenschutzerklärung von YouTube.
Mehr erfahren
Accurate key figures through video analysis
Stay one step ahead of your competitors with video analytics. Analyze the collected data and act instead of react. We provide the tools to shorten queues, direct customer crowds, play appropriate background music.
Open standards allow easy integration of third-party hardware and software.
Collect and analyze customer data
Make profitable changes to your store layout, staff allocation and marketing strategy based on accurate data and insights from your in-store cameras. Open standards allow us to connect your video system to a variety of third-party applications.
We help you develop solutions for your specific needs.
Turn prospects into buyers
Take control of daily operations in ways you never thought possible before. From audio announcements for long lines and empty shelves to situational messaging to individual shoppers to encourage them to complete a purchase.
By controlling music, you can create the perfect atmosphere for any situation.
You get a powerful platform to inform and influence your customers.
Protection and security
with video analysis
Sales success is directly related to your customers’ sense of security. Our IP video systems offer a comprehensive security concept that makes your business attractive to potential customers.

Mit dem Laden des Videos akzeptieren Sie die Datenschutzerklärung von YouTube.
Mehr erfahren
Protection of people and property
Deterrence can play an important role in loss prevention and retail security. VTIS provides full video coverage (sales floor, warehouse, staff rooms, parking lots, and more).
Video analytics can detect suspicious behavior and automatically alert security personnel or police. Of course, the privacy of your customers is protected by automatically masking their faces.
Security for your customers and employees
Accidents and violent incidents on your premises can have dire consequences for your customers, your staff and your reputation. Video analytics can detect and prevent unsafe situations. Audio analytics can detect aggressive behavior and automatically alert security personnel. Give your employees additional security by integrating panic alarms.
We can help you develop solutions for your specific needs.
Securing your premises
VTIS video systems offer you the right security solution for every part of your property. Anti-tailgating technology and visitor access systems help prevent unauthorized entry. Garages can be monitored with motion-activated cameras and license plate recognition. Cash rooms and storage areas can be protected with high-resolution cameras and network door controllers. And in your perimeter, you can install alarms or loudspeakers to deter loiterers.
We tailor your VTIS video system to your specific needs and requirements.
Protect property and people
with video analysis

Sales area
Automatically detect aggressive behavior and send alerts to security personnel.
Detect unauthorized occupancies to reduce vandalism and shoplifting.
Entrances & exits
Control entry and exit from your premises with visitor access systems connected to audio. Secure exits are not blocked.
Cash room
Restrict access to secure areas with software that recognizes, identifies, or verifies authorized personnel.
Warehouse & Loading Docks
Control access with access cards or QR codes, license plate recognition, congestion detection, and other automated methods. Use high-quality video to verify and track deliveries.
Parking spaces
Weatherproof, vandal-resistant cameras suitable for all lighting conditions protect customers and employees day and night. Deter unauthorized presence via voice messaging.